Back
Updated at: February 15, 2026
Embedded Finance and Banking-as-a-Service: Market Analysis 2025

In 2025, embedded finance and Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) have become some of the most transformative areas in financial services. Their market value has reached record levels, and regulatory frameworks are gradually adapting to support innovation while strengthening consumer protection.
The convergence of digital transformation, legislative harmonization, and growing demand for convenient financial services has created ideal conditions for exponential growth. Already in 2025, the embedded finance market is estimated at $148 billion, and by 2030, it is projected to grow to $639 billion.
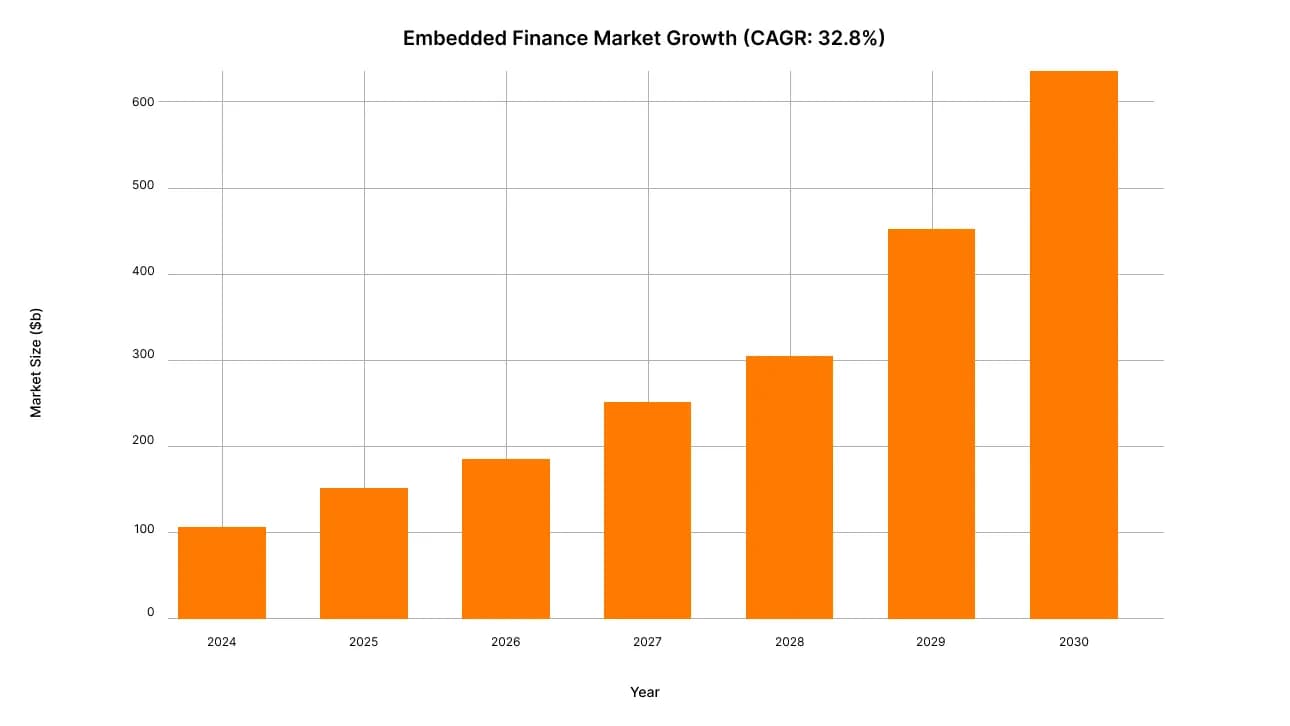
Global Embedded Finance Market Growth Projection (2024-2030)
Market landscape and growth dynamics
Current assessment and development trajectory
The global embedded finance market is showing impressive resilience: from $104.8 billion in 2024, it will grow to $148.4 billion in 2025, demonstrating a CAGR of 32.8%. By 2030, the volume is projected to reach $588–690 billion.
The BaaS segment is still smaller in absolute terms: $18.6 billion in 2024, but it is growing steadily, with a CAGR of 15.1%, and could reach $66 billion by 2030.
This growth is supported by several factors:
- growing demand for digital financial services;
- technological capabilities for seamless integration;
- the rapid development of e-commerce and the need for new payment solutions.
Geographical structure and regional dynamics
- North America maintains its leadership thanks to a developed fintech ecosystem. The US market alone exceeded $29.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $468.3 billion by 2034 (CAGR 31.85%).
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest growing region, with a projected CAGR of 26.45% through 2030. Growth is driven by mobile-first consumer behavior, super apps, and progressive initiatives such as UPI in India and PayNow in Singapore.
- Europe remains a significant player. The EU fintech market will reach $85.5 billion in 2025 and grow to $171.4 billion by 2030 (CAGR 14.9%). Regulatory initiatives PSD2 and the upcoming PSD3, which standardize APIs and simplify data exchange, play a key role here.
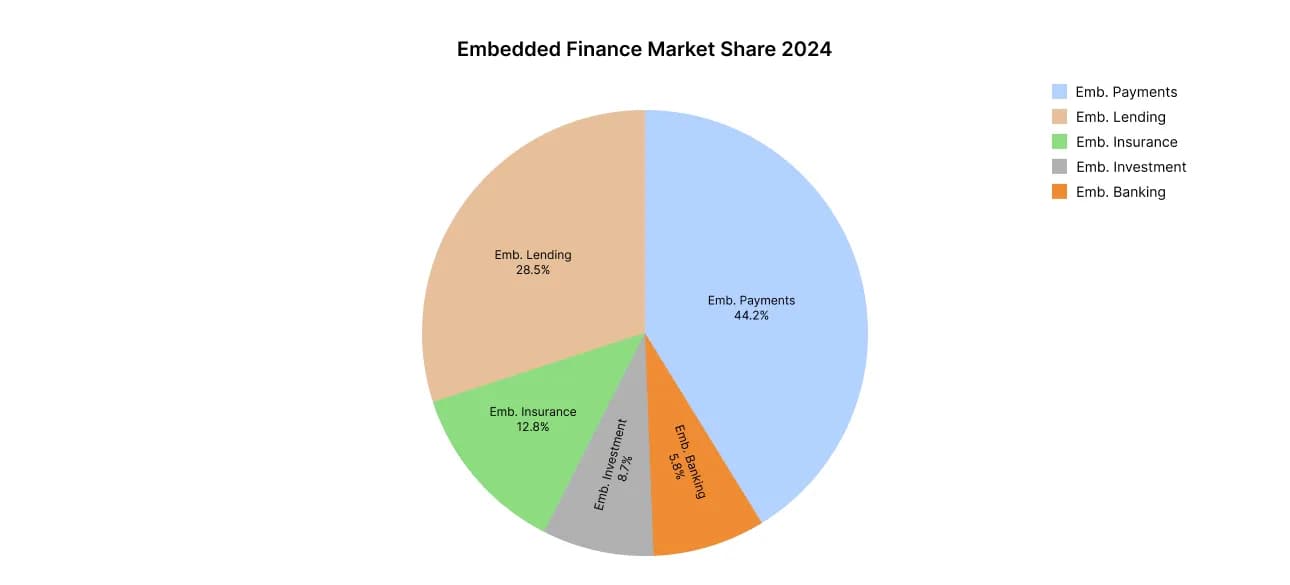
Embedded Finance Market Share by Service Type (2024)
Service segments and market structure
Dominance of the payments segment
Payment solutions account for the largest share of embedded finance, representing 44.2% of the market in 2024. Their success can be explained by:
- widespread adoption of embedded checkout systems,
- popularity of built-in wallets and cards,
- convenience and users' familiarity with digital payments.
Examples:
- Uber issues cards to drivers, allowing them to receive their earnings daily rather than monthly.
- Shopify has evolved from an e-commerce platform into a financial services ecosystem. Built-in payments have become a major source of revenue thanks to Shop Pay, Shopify Balance, and Shopify Capital.
New segments and growth opportunities
- Built-in investments are the fastest-growing segment (CAGR 28.5% through 2030). Drivers include:
- AI advisors,
- the ability to make fractional investments directly in apps,
- super apps with automated portfolio management.
- Built-in lending is also actively developing. Particular attention is paid to Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) models and working capital financing for businesses.
According to McKinsey, embedded channels already account for 5–6% of retail and SME lending revenue in Europe (2023), and by 2030, their share could grow to 20–25%.
This growth is linked to the development of credit risk assessment algorithms and growing demand for contextual lending embedded in digital services.
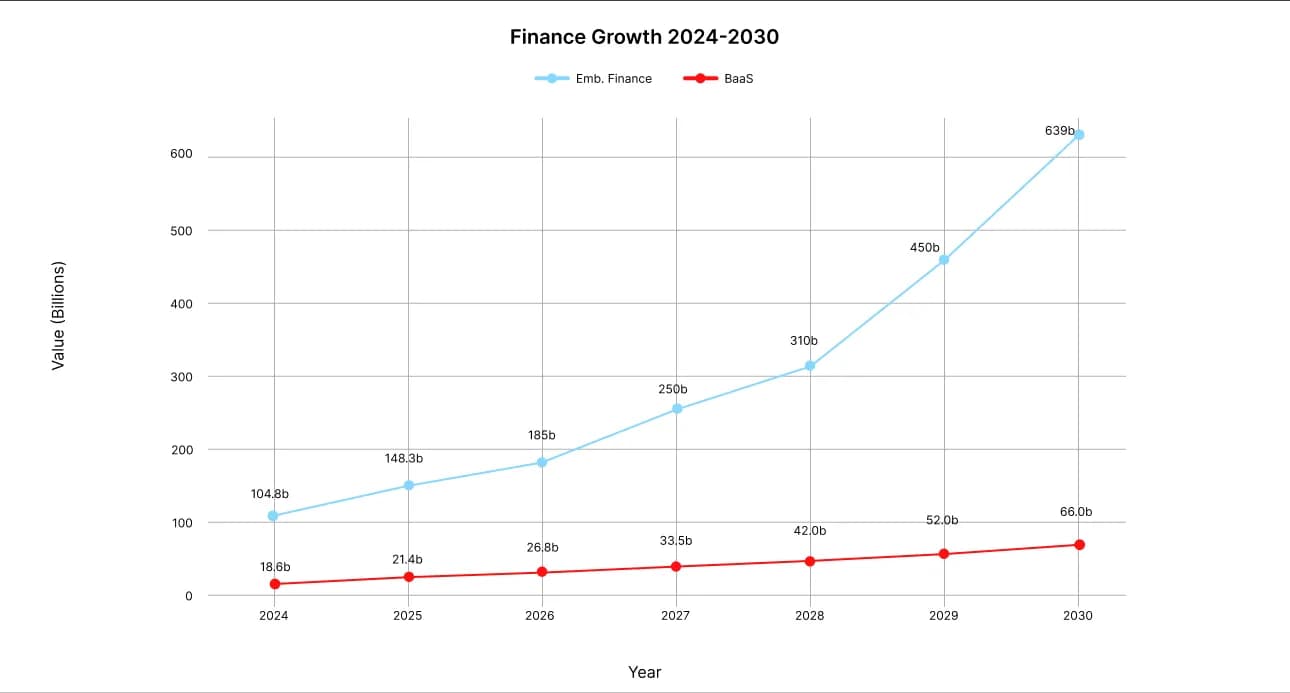
Embedded Finance vs BaaS Market Growth Comparison (2024-2030)
The evolution of regulation and compliance in Europe
PSD2 — the foundation for embedded finance
Adopted in 2018, PSD2 introduced strong customer authentication (SCA) and enabled secure data exchange between banks and third-party providers.
Key effects:
- emergence of standardized APIs;
- fair access to banking data with explicit customer consent;
- growth of new services: account aggregation, personal finance management, and contextual lending embedded in apps.
Challenges that remained: uneven implementation quality across EU markets and variability of bank APIs, which complicated cross-border solutions.
PSD3 — the next regulatory step
The upcoming PSD3 (expected 2026–2027) aims to close PSD2 gaps and broaden scope to instant payments, BNPL, and crypto transactions.
Planned improvements:
- uniform API standards across member states;
- stricter operational resilience and cybersecurity requirements;
- enhanced anti-fraud mechanisms;
- clearer liability rules for unauthorized transactions and refund processes.
Result: higher trust, easier multi-market rollout for embedded finance, and a more level playing field for providers.З
Wero — Europe’s digital sovereignty push
Wero is positioned as a pan-European digital wallet built atop SEPA Instant Credit Transfer. Backed by a consortium of leading EU banks, the initiative targets:
- wider interoperability across countries and banks;
- lower acceptance costs for merchants vs legacy rails;
- a trusted, EU-native alternative to global wallets.
Early milestones cited include multi-million users and transactions in Germany, France, and Belgium, with a roadmap to expand coverage to more EU markets through 2027.
Success stories and market leaders
Leaders in the US
The American embedded finance market showcases several remarkable examples:
- Stripe — a key player in embedded payments. With Stripe Connect and Stripe Treasury, the company provides ready-made APIs for payments, card issuance, and banking services. Its focus on developer experience and global reach made Stripe a standard for fast financial integration.
- Airwallex — a global infrastructure platform operating in 60+ markets with payouts to 200+ countries. Its solution integrates multi-currency accounts, FX, card issuing, and treasury management through a single API. Clients such as TradeBridge and Meow show the flexibility of its B2B model.
European fintech innovators
Europe has produced a number of embedded finance leaders:
- Klarna (Sweden) pioneered BNPL, evolving into a full embedded finance platform with personalized payment solutions for global retailers.
- Revolut illustrates the move from digital bank to financial super app, investing €1B into the French market and pursuing a banking license.
- N26 emphasizes UX simplicity and transparent pricing, winning millions of customers across Europe.
Platform integration case studies
- Shopify — a prime example of platform-to-fintech evolution. With Shopify Capital, Shop Pay, and Shopify Balance, financial services have become its main revenue driver.
- DoorDash + Parafin — a B2B success story. Restaurants can access financing within 24–48h, with repayments tied to performance metrics. This integration enhances merchant loyalty and creates new revenue streams for the platform.
Technical implementation and integration models
Payment integration architectures
Modern embedded finance implementations rely on RESTful APIs, enabling secure and scalable integration of banking services into non-financial platforms.
Banking-as-a-Service providers typically offer modular APIs for:
- account creation,
- transactions,
- card issuance,
- regulatory compliance.
Security and trust are ensured through tokenization, encryption, and real-time fraud monitoring. Providers such as ClearBank and Solaris offer comprehensive API suites that enable fast deployment without heavy in-house development.
Integration into vertical SaaS platforms
Vertical SaaS applications across industries increasingly integrate embedded finance to create added value and new revenue streams.
Examples:
- Healthcare platforms: patient financing and insurance verification.
- Construction software: equipment financing and payment processing.
Such implementations often involve:
- multi-party payment flows,
- automated reconciliation,
- multi-currency support and FX hedging,
- real-time cash flow analytics.
Integration into marketplaces and ecosystems
Digital marketplaces are natural environments for embedded finance, as they connect buyers and sellers and can offer comprehensive financial services to both.
Typical scenarios:
- seller financing,
- instant payouts,
- integrated payments with transaction transparency.
Example: eBay’s Capital for eBay Business Sellers program, powered by YouLend, showed that financed businesses grew their GMV by 26% compared to peers — proving how embedded finance boosts both merchant performance and platform revenues.
Investment landscape and trends
Global investment patterns
The global fintech sector attracted $44.7 billion across 2,216 deals in H1 2025, down from $54.2 billion in H2 2024.
This decline hides uneven dynamics:
- embedded finance and AI-enabled fintech continue to draw strong investor interest,
- while traditional payments received less attention ($4.6B in H1 2025 vs $30.8B in 2024).
AI applications in fintech are especially attractive. They raised $7.2B in H1 2025 compared to $8.9B in 2024. Solutions based on agentic AI — capable of executing multi-step tasks with real-time analytics — are of particular interest.
Funding in Europe
European fintech funding remained resilient, raising €5.2 billion in H1 2025.
- The UK retained leadership, attracting €2.5B (48% of the total) across 74 deals.
- 4 of the 10 largest European deals were debt financing, showing appetite for structured capital, particularly in lending and consumer finance.
The diversity of investment is growing, spanning climate fintech, wealth management, payments, and embedded finance. This highlights both sector maturity and the broad application of embedded principles.
M&A and strategic alliances
Mergers and acquisitions in embedded finance are focused on building full-stack platforms and strengthening real-time payment capabilities.
Goals:
- expand payment rails,
- acquire licenses for new regions,
- increase cross-border capabilities.
Example: Green Dot launched Arc, combining embedded finance and BaaS into a single platform — showing how even traditional players are actively positioning themselves in this fast-growing segment.
Forecasts and long-term prospects
Long-term forecasts
Analysts predict that embedded finance will radically reshape financial services by 2030, with market potential of up to $7.2 trillion.
This transformation reflects not only market expansion but also the deep integration of financial services into daily business and consumer activities.
The expected evolution phases:
- Payment integration,
- Expansion into lending, insurance, and investment,
- Full financial ecosystems including treasury services.
Ultimately, embedded finance will no longer be a niche category, but rather core infrastructure for most digital business models.
Regional differences in growth
- APAC will lead in growth, driven by mobile-first behavior, super apps, and regulatory support. India, boosted by UPI, may reach a CAGR of 45% in embedded finance.
- Europe will benefit from regulatory harmonization under PSD3 and expansion of pan-European solutions like Wero. This will accelerate cross-border integration and strengthen B2B and vertical SaaS use cases.
- US will continue to lead in infrastructure providers and technological capabilities.
Technological trends and innovations
AI-driven personalization
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming the core enabler of embedded finance.
- Personalization engines analyze user behavior and adapt financial offers in real time.
- Agentic AI systems can independently manage loan approval, portfolio balancing, or insurance recommendations, without direct human input.
Blockchain and DLT
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT) are enhancing:
- settlement speed,
- transparency of transactions,
- reduction of counterparty risks.
Several providers experiment with tokenized deposits and stablecoin-based settlement layers, expanding the B2B potential of embedded finance.
Quantum-powered anti-fraud
Emerging quantum algorithms provide advanced anomaly detection and risk modeling. Although still in pilot stages, they promise to boost fraud prevention for high-volume embedded platforms.
ESG and climate fintech
The growth of climate-conscious finance is accelerating:
- green loans,
- carbon footprint calculators,
- sustainable investment portfolios.
This trend integrates directly into e-commerce, mobility, and real estate platforms, where embedded models make ESG compliance both visible and actionable.
Strategic recommendations
For traditional banks
- Treat embedded finance not as a threat, but as a strategic opportunity.
- Build own Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) platforms or establish partnerships with fintechs to stay relevant.
- Invest in API standardization, compliance automation, and fraud monitoring to be PSD3-ready.
- Shift from a product-centric to a platform-centric mindset.
For non-financial companies
- Integrate financial services directly into core customer journeys (retail, mobility, healthcare, SaaS).
- Select partners based on regulatory reliability, scalability, and geographical coverage.
- Consider the impact on customer relationships: who owns the data, and who controls the end-user experience?
- Monetize financial flows through contextual offers (lending, insurance, payments) rather than treating them as auxiliary services.
For regulators and policymakers
- Support API harmonization and cross-border interoperability to foster innovation.
- Strengthen cybersecurity frameworks without stifling agile fintech models.
- Ensure consumer protection and transparency in BNPL, instant payments, and crypto-linked services.
- Encourage collaboration between banks and fintechs under controlled sandbox environments.
BaaS provider selection matrix (2025)
|
Provider |
Geography |
Strengths |
Limitations |
Clients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
US, global |
Rich APIs (Connect, Treasury), scalability |
Higher cost at scale |
SaaS, e-commerce | |
|
Asia, EU, US |
Multi-currency, payouts to 200+ countries |
Limited B2C focus |
B2B, fintechs | |
|
Europe |
Full-stack BaaS, EU license, compliance |
EU-only focus |
Neobanks, SaaS | |
|
UK, EU |
Strong payments, real-time processing |
Not full-stack |
Banks, fintechs | |
|
US, global |
Card issuing, tokenization |
Card-centric model |
BNPL, fintechs | |
|
Europe, Asia |
Wide API coverage, flexible integration |
Restructuring challenges |
Startups | |
|
Europe, US |
White-label, strong partnerships |
Higher operational cost |
Corporates | |
|
US |
Simple API, compliance-focused |
US-only |
SaaS, fintechs | |
|
Global |
Core banking-as-a-service |
Complex integration |
Banks, platforms |
Summary of positioning:
- Global scaling: Airwallex, Stripe, Marqeta.
- Europe / PSD2–PSD3 alignment: Solaris, ClearBank, Railsr.
- US & fast launch: Unit, Stripe.
- Flexibility & customization: Mambu, Bankable.
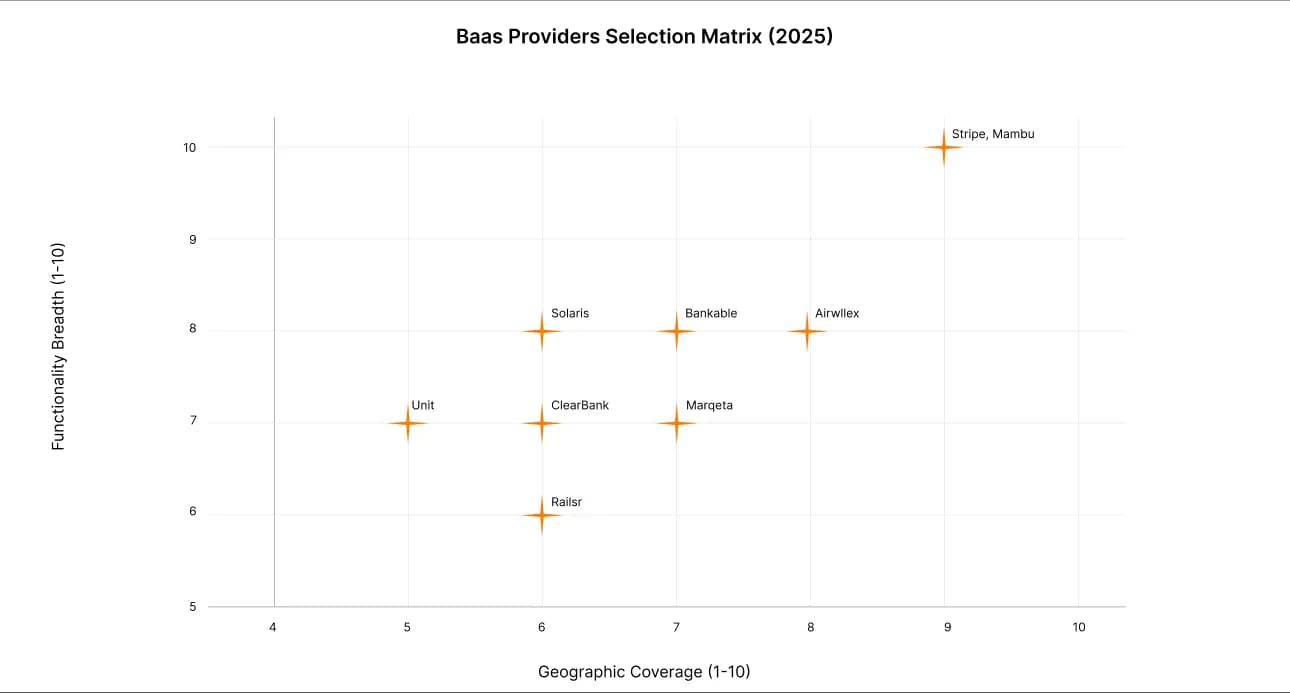
Providers positioning matrix
Conclusion
Embedded finance and Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) are no longer just trends — they represent a structural transformation of the financial industry.
Key takeaways:
- They enable new revenue models and deeper customer engagement for both banks and non-financial companies.
- Regulatory frameworks (PSD2, upcoming PSD3) and pan-European initiatives like Wero are creating a foundation for trust and scalability.
- Technological enablers — AI, blockchain, quantum computing, and ESG integration — are accelerating adoption.
Those who act now can secure:
- long-term competitiveness,
- new growth opportunities,
- and a role as strategic partners in the financial value chain.
Those who delay risk being reduced to infrastructure providers, losing direct customer relationships and strategic influence.
The conclusion is clear: embedded finance is becoming a new digital layer of the global economy. Companies that embrace it will define the financial landscape of the next decade.
Summary:
Embedded finance and Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) have emerged as pivotal elements in the financial services sector, exhibiting significant market growth and innovation. The embedded finance market is projected to grow substantially, driven by the increasing demand for digital financial services and advancements in technology. North America leads this trend, supported by a robust fintech ecosystem, while the Asia-Pacific region is noted for its rapid expansion fueled by mobile-first consumer behavior. Payments remain the dominant segment within embedded finance, although built-in investments and lending solutions, particularly Buy Now Pay Later models, are showing fast growth. Regulatory frameworks like the PSD2 and the anticipated PSD3 are enhancing consumer protection and fostering a competitive environment in Europe. Companies such as Stripe and Klarna are exemplars of success in this space, leveraging their platforms to integrate financial services seamlessly. Investment in fintech, especially in embedded finance and AI-driven solutions, remains strong, despite a general decline in funding across the sector. Emerging technologies, including AI and blockchain, are set to further transform the financial landscape by enhancing efficiency and personalization in financial services. As embedded finance becomes more integrated into everyday business operations, it is expected to redefine traditional banking models and create new revenue streams. Organizations that adapt to these changes will likely secure a competitive edge in the evolving financial ecosystem.
Read also:
embeddedfinance
bankingasaservice
baas
fintech
financialservices
digitalbanking
marketanalysis2025
fintechtrends
embeddedpayments
financialinnovation
fintechmarket
globalfinance
aiinfinance
blockchainfinance
psd2
psd3
financialregulation
europeanfintech
apacfintech
usfintech
investmenttrends
fintechecosystem




