Back
Updated at: October 17, 2025
Real-time as a standard: event-driven architecture for millions of events

User expectations have changed radically. Today, instant responses, personalization in fractions of a second, and continuous service availability have become the norm. New generation companies like Netflix, Uber, and Airbnb achieved this thanks to an event-driven architecture (EDA) based on technologies like Apache Kafka, event sourcing, and CQRS.
This is precisely the approach that allowed them to achieve scalability, performance, and fault tolerance that seemed impossible just recently. Modern platforms and trading systems process millions of events per second, providing almost limitless scalability and error-free real-time operation. This is a technical achievement, and it's fundamentally restructuring business models, where technology directly determines efficiency and success.
From monolith to real-time systems
Real-time systems are no longer considered a competitive advantage – today they have become the foundation of digital business.
According to a study by MIT CISR, companies operating in real time demonstrate 62% higher revenue growth and 97% higher profit levels than their slower competitors.
The capacity to respond instantly to market signals, user actions, and internal system events is a new strategic objective. From streaming services to trading platforms, it's the speed of reaction that now determines who will survive in the market.
Traditional monolithic architectures and batch data processing are no longer able to keep up with the required pace. The world has entered an era of continuous interaction, where every signal and every event can become a decision-making moment – or a missed opportunity.
Why Event-Driven Architecture is a Hot Trend for 2025: A Technical and Business Perspective
What makes EDA indispensable?
Event-driven architecture (EDA) is radically changing the dynamics of modern systems, turning any significant change into an event that can be processed and used for decision-making.
EDA is based on Apache Kafka, which provides incredible throughput: on a cloud infrastructure, Kafka consistently demonstrates over 1 million messages per second, and companies like Shopify record up to 66 million messages per second during peak loads.
A combination of technologies achieves and enhances this performance:
- Event Sourcing – storing the complete history of state changes, ensuring transparency and auditability;
- CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) – separating write and read operations to optimize queries;
- Microservices – a modular structure that enables horizontal scaling and failure isolation.
Together, these components create an architecture where each element operates independently, but the entire system functions like a living organism, responding to events instantly and without performance loss.
Key business advantages
- Instant Response: EDA-based systems respond in less than a second, but traditional systems take more than a second. Studies show that Kafka and Pub/Sub designs have delays of 50 to 212 ms.
- Virtually unlimited scalability: EDA has almost infinite boundaries and scales linearly. A good example is when CrowdStrike distributes Kafka among hundreds of brokers, processing about 15 million events per second and trillions of them weekly.
- Better User Experience: Such things as personalized suggestions, real-time ride matching, and dynamic marketing became possible by event-driven platforms. Conversions increased fourfold as a result of switching to a real-time infrastructure (according to BNP Paribas Bank).
- Self-healing and fault tolerance: Event stream decoupling makes it sure that the failure of one service does not impact the others. Such systems are robust and resilient even under high loads thanks to techniques like circuit breakers, idempotency, redundant brokers, and automatic retries.
Actual figures and industry data
- Spotify processes 8 million events per second worldwide – over 500 billion events per day with consistent latency and support for 500+ types of event. This allows the platform to update analytics, royalty calculations, and new feature releases just in real-time.
- Netflix uses the Open Connect CDN and Kafka pipelines, combining local caching and adaptive routing for seamless content playback all over the world. Every day, their infrastructure processes billions of events, ensuring a smooth user experience without delays.
How the event stream works
EDA platforms receive event streams – from users, systems, and market sources – thru independent event producers. The data is then routed thru an event broker (Kafka), and consumers (analytical services, risk control systems, order matching, etc.) process the events asynchronously. Monitoring and failover systems ensure stability under extreme loads.
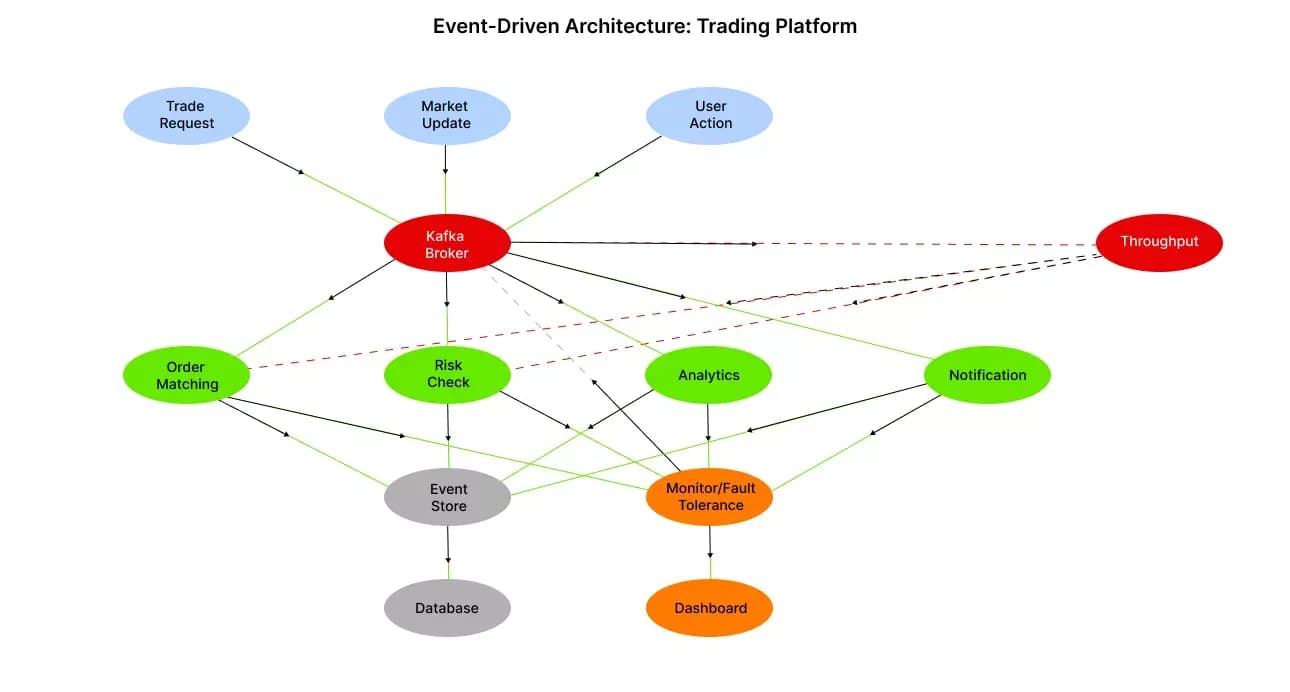
Event-Driven Architecture Flow for Real-Time Trading Platform
The comparison shows an exponential difference: Monolithic systems stop at thousands of events per second with a delay of over 1 second, while Kafka and Big Tech architectures consistently handle millions of events per second with a delay of less than 100ms.
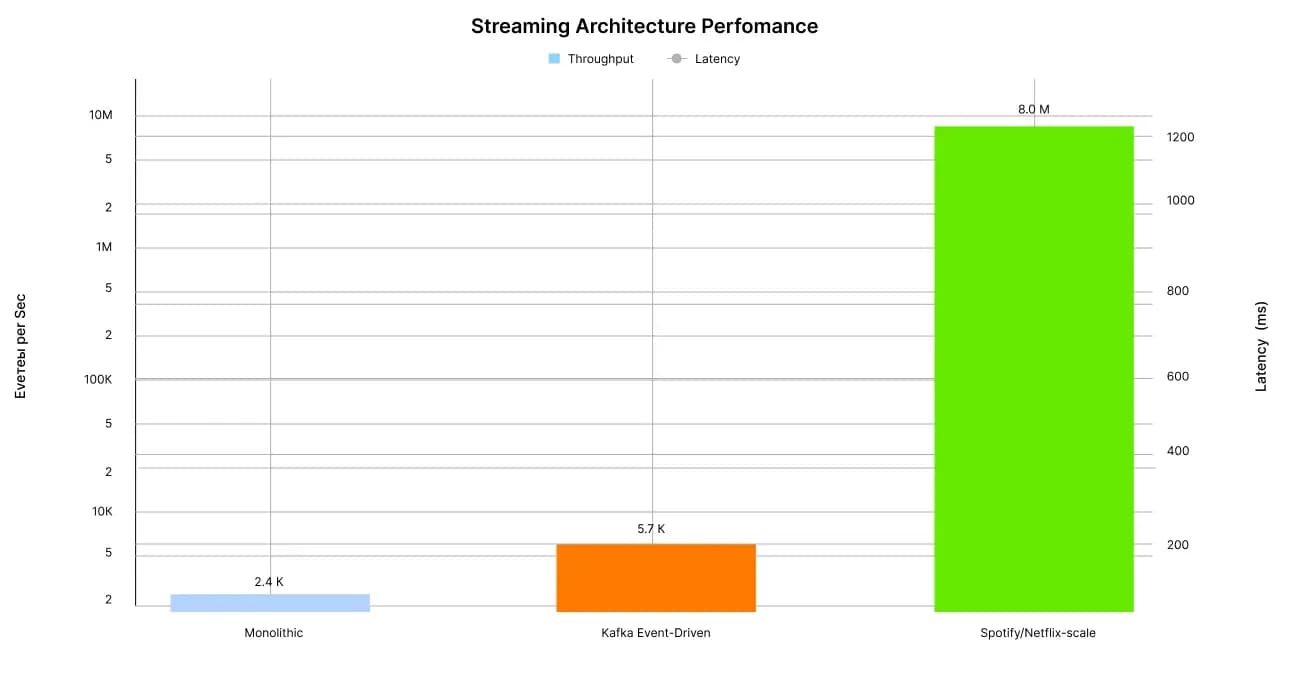
Throughput and Latency: Monolithic vs. Event-Driven vs. Big Tech
The event-driven approach is now the cornerstone of digital platforms, where every event counts and success is determined by response time, rather than being a specialized tool for engineers.
Analysis: How EDA Powers Scalable, Responsive Systems
Scalable Event Flow and Processing
Imagine the design where event producers (user actions, market data) are decoupled from event consumers (analytics, notifications, risk checks).
Apache Kafka’s log-based storage and partitioning provide immutable, highly available event records accessible in real time, allowing parallel scaling across nodes and teams.
Such a design enables instant horizontal expansion — without tight coupling, slow request/response bottlenecks, or risky monolithic dependencies.
System Reliability and Fault Tolerance
Techniques include redundant data centers (Netflix), partitioning/sharding of event streams (Spotify, CrowdStrike), and comprehensive observability frameworks.
All these ensure platforms remain resilient at scale.
Fault tolerance means errors do not cascade, and system recovery is supported via event replay, snapshotting, and robust monitoring.
Exactly-once semantics and idempotency safeguard financial accuracy and transactional integrity even in mission-critical environments like trading platforms and payments.
Real-World Architecture Snapshots
- Netflix Open Connect CDN moves content closer to consumers using a tiered network of distributed servers, enabling minimal latency and seamless video delivery.
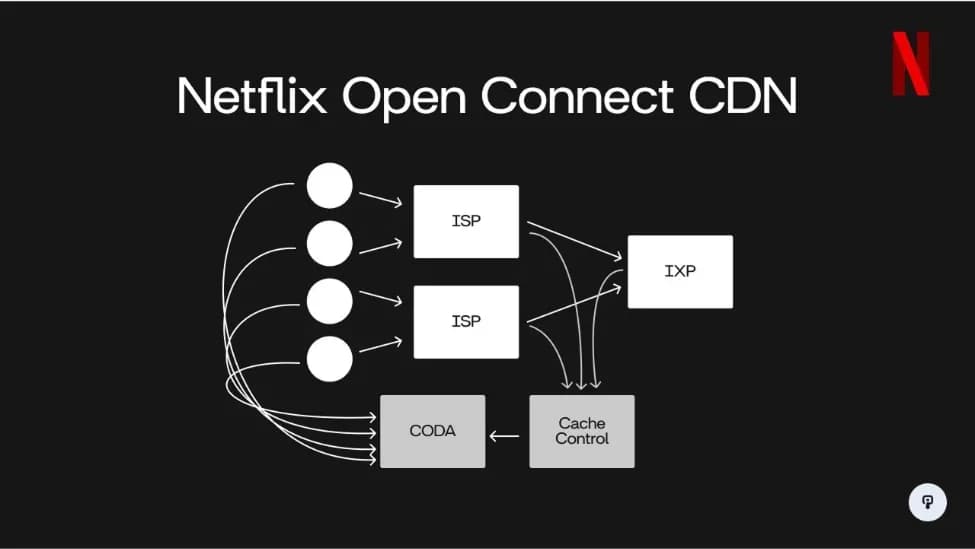
Diagram of Netflix Open Connect CDN architecture showing data flow from users through ISPs, IXP, cache control, and CODA systems.
- Uber’s event-driven architecture uses distributed caches and event streams to manage pricing, routing, matching, and ride requests in real time.
For fault isolation and scalability, each of the services works independently and consumes live events.
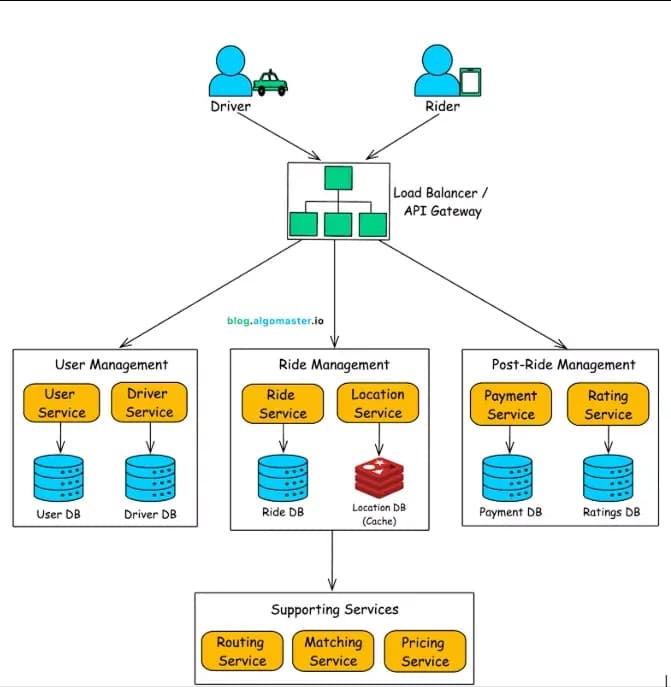
High-level architecture of Uber's event-driven ride-sharing system illustrating microservices and databases.
- Spotify’s event delivery system uses Google Cloud Pub/Sub to divide events into hourly buckets while maintaining strict verifiability, latency targets, and partition isolation across 500+ event types.
- Trading Platforms — architectures routinely handle over 1 million transactions/events per second with sub-millisecond execution latency, strict compliance (GDPR, financial regulations), and real-time analytics.
For instance, Nasdaq sets up co-located servers to provide zero downtime and sub-millisecond interventions, which are essential for high-frequency trading.
Microservices and Event Sourcing: How Companies Build Systems That Don't Break
Independent service architecture
The microservices approach, combined with event-driven architecture (EDA), provides what classic monoliths have long lacked: flexibility, fault tolerance, and manageable scaling.
Each service turns into a separate unit that can be grown, changed, and deployed without affecting the others. This eliminates the “domino effect”, where the failure of one module paralyzes the entire system in a chain reaction.
Event Sourcing technology complements this approach: every change in the system is recorded as a separate event, and the current state can be restored by “replaying” the history.
This is how companies gain:
- Instant recovery from failures;
- Full operation traceability (audit trail);
- Confidence in data integrity even under high load.
These principles have long been applied by Shopify, Amazon, and eBay – not just for stability, but also to ensure growth without downtime.
Examples of leaders building businesses around events
Shopify: Shopify processes up to 66 million messages per second using Apache Kafka, aggregating events from payment modules, inventory, and checkout.
Event-driven architecture allows the company to scale services independently during traffic peaks and effortlessly handle load spikes during periods like Black Friday.
SumUp: SumUp, an international payment platform, processes millions of transactions daily in over 30 countries. The infrastructure is built on Confluent Cloud (Kafka) and is fully managed as an event-driven environment: analytics, monitoring, and anti-fraud systems receive data in real time. The platform ensures uninterrupted operation and a high degree of security by scaling automatically during seasonal peaks.
CrowdStrike: The CrowdStrike cybersecurity system analyzes a trillion events per day. Thanks to Kafka’s sharding and a microservices architecture, the company achieves 15 million events per second with a processing latency of just a few milliseconds, ensuring an immediate response to threats.
Goldman Sachs: The trading systems of this investment giant rely on EDA. The system provides real-time trading decisions by analyzing billions of price and market events daily using Apache Kafka and Apache Flink. Thanks to AI analytics, the delay between the signal and trade execution is only 14 milliseconds, and the profitability of trading operations has increased by 27% compared to manual management.
SEO 2025: Trust, Expertise, and Speed of Discovery
In 2025, search algorithms (including Google) placed a stronger emphasis on the E-E-A-T concept – Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness.
For technical and industrial topics, this means that without transparent data, expert cases, and real sources, content loses ground.

Key elements of EEAT for creating credible, expert, and trustworthy online content.
Event-Driven Architecture (EDA) and real-world examples of its application are perfectly aligned with this model. Architectural transparency, measurable values, and credible success stories all naturally enhance brand authority.
2025's Top SEO Trends
- Semantic Search and Intent Optimization: AI-powered algorithms prefer content that provides context and answers actual queries rather than merely contains keywords.
- UX and Mobility as Ranking Elements: Search engines favor event-driven websites that respond instantly, have an adaptive design, and don't take too long to load.
- Data Transparency and Source Authority: Every mentioned fact must be supported by open metrics and references to reliable sources — such as Statista, Google, McKinsey, industry reports, and open platforms.
In addition to speeding up digital systems, EDA increases confidence for users and search engines.
Anything that doesn't update instantly gradually disappears from view in the real-time era.
Case Study: Real-Time Trading Platform – An Unfailing System
To understand how Event-Driven Architecture (EDA) unlocks its potential, one need only look at one of the most reliability-demanding industries – financial markets.
Over a million events per second must be processed by real-time trading systems, deals executed in milliseconds, and they must remain operational even during peak loads or partial infrastructure failures.
The architecture of such a system looks like this:
1. Event Producers (Event Sources)
The platform receives events from such sources as:
- Market feeds containing orders and quotations;
- Broker and user trading requests;
- Customer actions, including position adjustments, limits, and strategies.
Every event enters the stream instantly, without delays or batch processing.
2. Broker of Events
Apache Kafka, a reliable and resilient event broker, sits at the heart of the system.
Kafka guarantees that no messages are lost, even in the event of a data center outage or any node failure.
3. Event Consumers
Data streams are processed in parallel, asynchronously, and individually by specialized services.
- The matching engine provides quick order matching and trade execution;
- The risk checker examines limits and market volatility;
- The analytics and notifications system produces real-time reports, alerts, and aggregated data.
4. Audit Trail
Using Event Sourcing, the system logs each state change as a separate event.
Consequently, it generates a valid and unalterable transaction record.
As a result, the platform is able to reconstruct the complete transaction history, down to the very last byte.
5. Vigilance and Adaptability
Mechanisms for self-healing and observability work in a proactive manner:
- Circuit breakers automatically isolate malfunctioning processes;
- Self-healing restarts them without operator assistance;
- Real-time flow metrics analysis stops performance degradation.
Peak load resilience is a feature of EDA, guaranteeing platform operation even when data volume increases multiple times.
6. Sub-Second Latency
Even with millions of events per second, the system maintains sub-second latency.
In-memory analytics, compliance-level checkpoints, and asynchronous processing streams enable entire execution cycles to complete in less than a second.
EDA demonstrates that, with proper architecture design, “never falling” is an engineering standard rather than a marketing slogan.
In addition, next-generation trading platforms foresee setbacks, automatically recover, and scale infinitely
Conclusion and Practical Recommendations
Key Findings
Event-Driven Architecture (EDA) has proven its ability to deliver measurable business value:
- Instant (sub-second) response even under extreme loads;
- Limitless scalability, where traffic growth doesn’t mean increased costs;
- Improved user experience thanks to reactive systems;
- Built-in fault tolerance, eliminating single points of failure.
EDA relies on Apache Kafka, Event Sourcing, and CQRS – the three cornerstones of modern digital architecture.
Leading e-commerce platforms such as Netflix, Uber, and Airbnb use these patterns to guarantee data integrity, process dependability, and top-notch performance.
EDA scalability is an established practice rather than a theory.
Real-world benchmarks show that systems based on it process millions and tens of millions of events per second, maintaining latency below one second and global fault isolation in production environments.
EDA doesn’t just speed up systems – it creates a new class of business models where real-time becomes the operational standard.
Recommendations for Companies
- Need to examine the current architecture and evaluate infrastructure readiness for real-time operations.
If latency, fault tolerance, or scalability remain bottlenecks, it’s time to switch to an event-driven approach. - CQRS, Event Sourcing, and Apache Kafka are essential.
These technologies are ideal for applications that require high throughput, data consistency, and regulatory compliance. - Invest in observability, resilience, data contracts, system health metrics, and automated recovery.
This ensures compliance with Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and enables rapid incident response. - Stay ahead of SEO trends in 2025 and promote technical content with a focus on expertise, transparency, and trust.
Support publications with data, benchmarks, and real-world examples, citing trusted sources such as Statista, McKinsey, Confluent and Google Cloud.
Begin with pilot projects.
Implement EDA in trading operations, recommendations, and payments – three critical areas for any digital enterprise.
Once testing is successful, implement the model throughout the entire company.
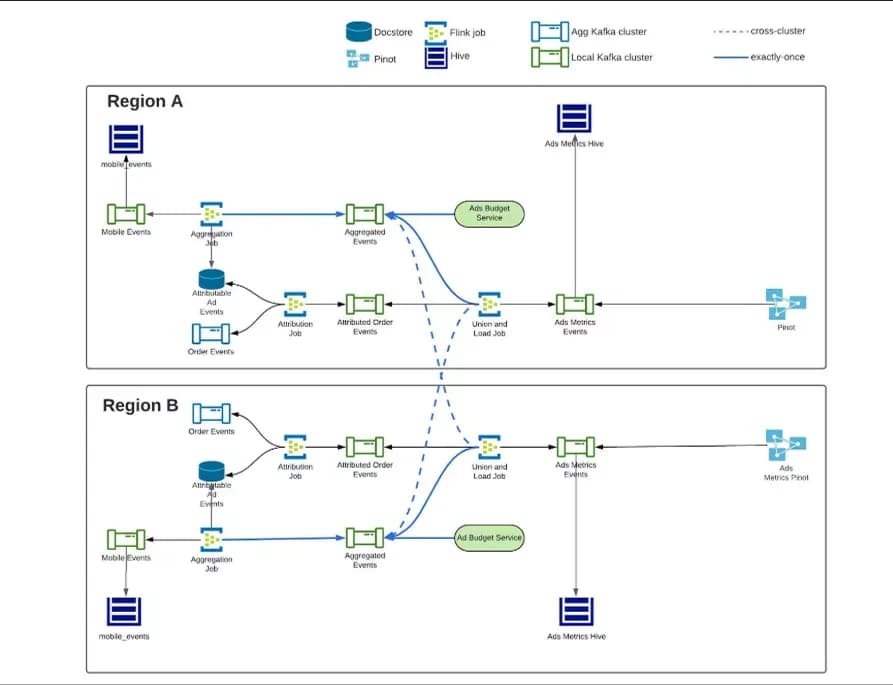
Architecture diagram illustrating real-time exactly-once ad event processing with Apache Flink and Kafka clusters in a distributed event-driven system.
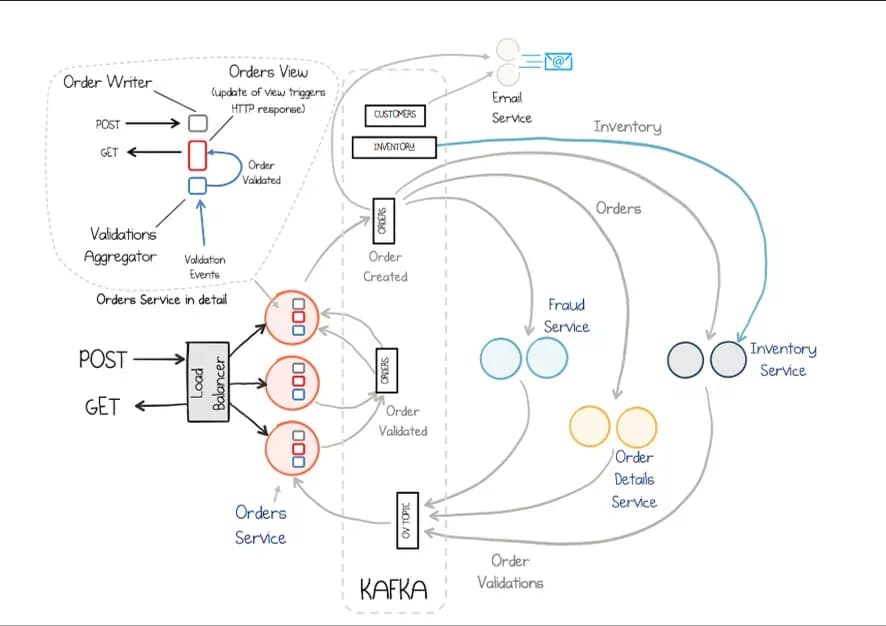
Microservices event-driven architecture with Apache Kafka illustrating real-time order processing and service communication.
The Final Touch
Event-driven architecture is now a strategic requirement for any business aiming to dominate the digital market, not just a fad.
EDA allows you to build systems that never go down, respond instantly, and scale alongside your business.
Call to Action
If you want your digital platform to operate in real time, handle millions of events per second, and remain resilient under extreme loads, it’s time to move to the architecture of the future today.
We Can Develop IT will help you design and implement a custom event-driven solution that will elevate your business into the category of companies that don’t just keep up — they set the pace of the market.
Summary:
User expectations for instant responses and continuous service availability have led to the rise of event-driven architecture (EDA) in modern businesses. Companies like Netflix, Uber, and Airbnb leverage EDA, utilizing technologies such as Apache Kafka and CQRS to achieve unprecedented scalability and performance. The shift from traditional monolithic systems to real-time architectures has become essential for digital competitiveness, with research indicating that real-time companies experience significantly higher revenue and profit growth. EDA enables instantaneous processing of millions of events per second, facilitating better user experiences through features like personalized recommendations and real-time analytics. It incorporates principles like event sourcing and microservices to create flexible, fault-tolerant systems that can adapt rapidly and operate independently. Major platforms, such as Spotify and CrowdStrike, exemplify the capabilities of EDA, processing vast amounts of data with minimal latency and high reliability. Moreover, EDA enhances operational transparency and data integrity, which are crucial for maintaining trust and compliance in regulated industries. As EDA becomes the industry standard, businesses are encouraged to reassess their architectures and embrace this model to remain competitive. The implementation of EDA is seen as a strategic necessity for organizations aiming to thrive in the digital landscape. Transitioning to this architecture not only improves system performance but also fosters innovative business models that prioritize real-time operations.
Read also:
eventdrivenarchitecture
EDA
realtimearchitecture
realtimesystems
ApacheKafka
eventstreaming
eventsourcing
CQRS
microservices
scalability
systemdesign
cloudarchitecture
datastreaming
asynchronousprocessing
faulttolerance
highavailability
Netflixarchitecture
UberEDA
AirbnbEDA
ShopifyKafka
CrowdStrikeKafka
GoldmanSachsEDA
ConfluentCloud
realtimeanalytics
distributedarchitecture
systemresilience
techinnovation
softwareengineering
systemperformance
realtimetradingplatform
financialsystems
datainfrastructure
highthroughput
lowlatency
exactlyoncesemantics
systemreliability
scalableplatforms
digitaltransformation
datadrivenbusiness
AIinfrastructure
2025techtrends
systemoptimization
engineeringbestpractices
EEAT
SEO2025
expertcontent
trustworthycontent
technicalarchitecture
businessscalability
platformresilience




